From PE (polyethylene) to PET (polyethylene terephthalate), when the film slitting machine adapts to different materials, it needs to be systematically adjusted from the key links such as mechanical structure, process parameters, tool design, and tension control. The following are the specific adaptation strategies:
First, the core adaptation principle
The modulus of elasticity, thermal shrinkage, and surface characteristics of the film material determine the adjustment direction of the slitting machine. For example:
• PE: low elastic modulus (0.1-0.3GPa), easy to stretch, low tension, blunt knife slitting;
• PET: High modulus of elasticity (3-5GPa), good dimensional stability, high tension, sharp blades are required.

Second, the mechanical structure adjustment
1. Tooling system
• Blade material: carbon steel blade for PE (low cost), carbide blade for PET (good wear resistance).
• Blade angle: 15°-20° shallow angle for PE to reduce cutting resistance; PET uses an acute angle of 25°-30° to ensure a smooth cutting surface.
• Tool pitch adjustment: dynamically adjusted according to the film thickness, PET slitting needs to be smaller tool pitch (e.g. 0.1-0.3mm).
2. Slitting roller design
• Roll surface roughness: Ra 0.8-1.6μm for PE (anti-slip), Ra0.4-0.8μm for PET (anti-scratch).
• Roller material: aluminum alloy for PE (lightweight), steel for PET (high rigidity).
3. Optimization of process parameters
| parameter | PE adaptation | PET adaptation |
| Tension control | 5-15N/m (low tension and anti-deformation) | 20-50N/m (high tension anti-wrinkle) |
| Slitting speed | 100-200m/min (low-speed anti-breakage film) | 300-500m/min (high-speed accuracy) |
| Temperature control | No heating required (room temperature slitting) | Roller heating to 40-60°C (reduced brittleness) |
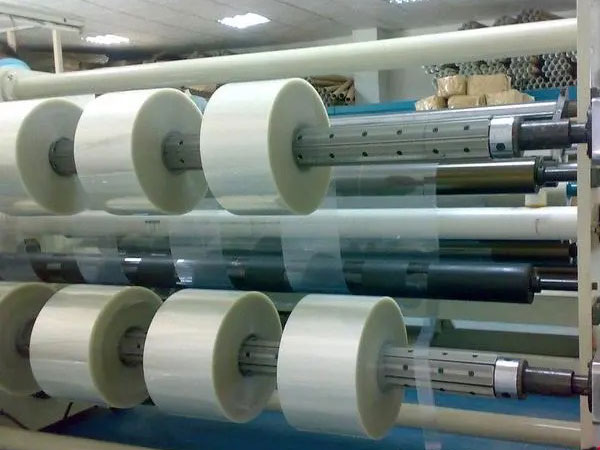

Fourth, tension control strategy
1. Tension sensor: real-time monitoring of film tension, PET needs to dynamically compensate for the tension fluctuation caused by heat shrinkage.
2. Winding method:
• PE: Center coiling (high tolerance for tension fluctuations);
• PET: Surface winding (requires high-precision tension closed-loop control).
5. Case analysis
• A food packaging factory: When switching from PE to PET, the slitting speed was increased from 180 m/min to 400 m/min, the tension was increased from 12 N/m to 35 N/m, the blade angle was adjusted from 18° to 28°, and the slitting defect rate was reduced from 8% to 0.5%.
• An electronic film factory: For PET film, infrared heating rollers were introduced to reduce the thermal shrinkage rate from 1.2% to 0.3%, and the burrs on the slitting edge were reduced by 70%.

6. Precautions
1. Transition material test: Before the official switching, it is necessary to use 100-200 meters to test the machine and record the best combination of parameters.
2. Tool life management: After PET slitting, the blade needs to be ground regularly (recommended every 5000 meters), and the PE slitting blade can be extended to 10000 meters.
3. Environmental control: The humidity of the PET slitting workshop needs to be ≤50% (anti-static), and the humidity of PE slitting can be relaxed to 60%.
7. Suggestions for technology upgrading
• Intelligent slitting system: integrated AI visual inspection, automatic identification of materials and adjustment of parameters;
• Modular tool magazine: Automatically switch insert types according to the material, reducing manual intervention.
Through the above adaptation strategy, the film slitting machine can realize seamless switching from PE to PET, the slitting efficiency is increased by 30%-50%, and the defective rate is reduced to less than 1%.
 Hot stamping paper slitting machine: a "silky" game in millimeters
Hot stamping paper slitting machine: a "silky" game in millimeters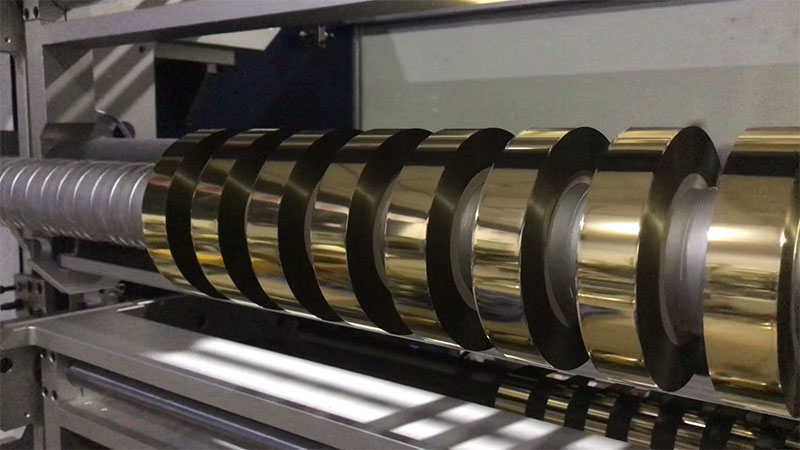 Hot stamping paper slitting machine: in the millimeter, carving the ultimate beauty
Hot stamping paper slitting machine: in the millimeter, carving the ultimate beauty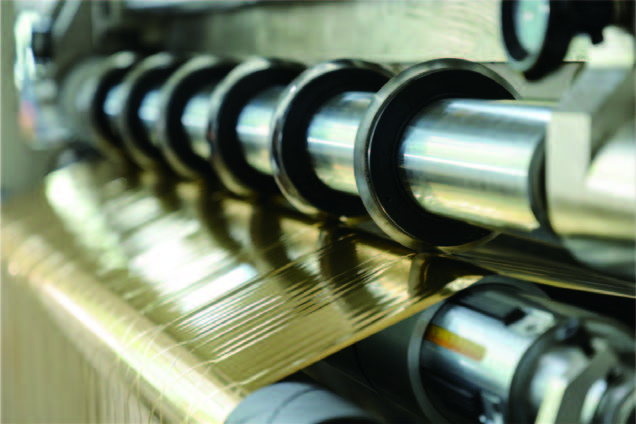 Say goodbye to burr dust: how a new generation of hot stamping paper slitting machines is reshaping industry standards
Say goodbye to burr dust: how a new generation of hot stamping paper slitting machines is reshaping industry standards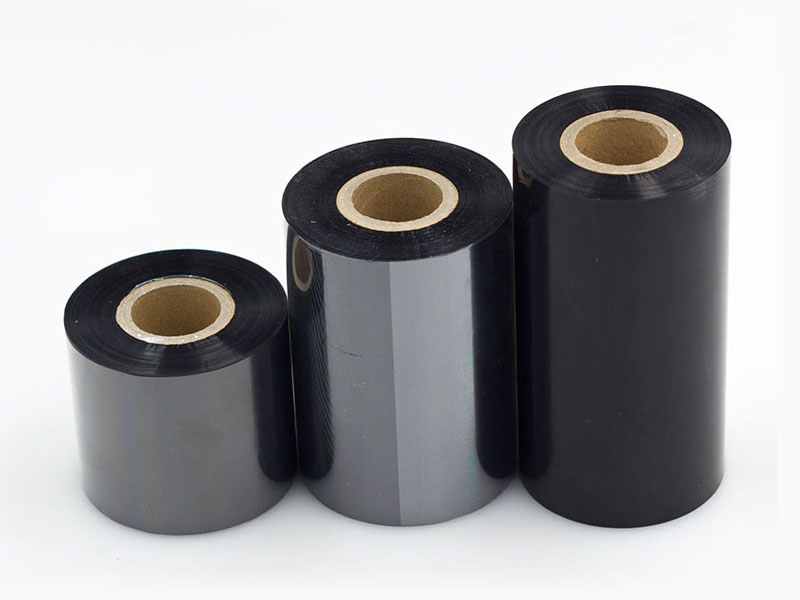 Intelligent control of tension, perfect winding: the core technology of the ribbon slitting machine is revealed
Intelligent control of tension, perfect winding: the core technology of the ribbon slitting machine is revealed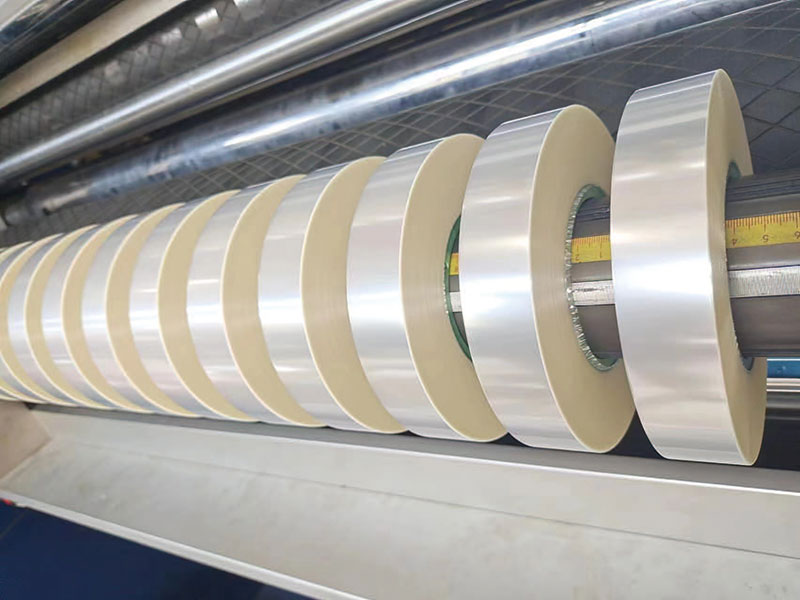 PET film slitting machine upgrade solution: the key to improving accuracy and speed
PET film slitting machine upgrade solution: the key to improving accuracy and speed