In the era of intelligent slitting, the collaborative application of PLC (programmable logic controller) and human-machine interface (HMI) has greatly simplified the operation process of the slitting machine, while improving the accuracy and efficiency. The following is the core optimization logic and how to implement it:
1. The collaborative working principle of PLC+HMI
1. PLC: As the control center, it is responsible for processing sensor data (tension, speed, position) in real time, executing logic operations, and outputting instructions to control motors, cylinders, tools and other actuators.
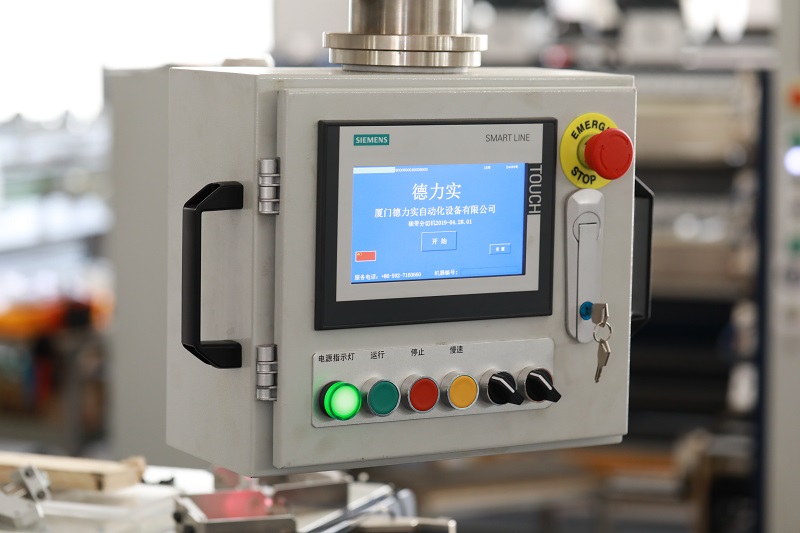
2. HMI: Acts as an interactive window to visualize complex parameters, allowing the operator to quickly set up and adjust the process via the touch screen.
◦ Data flow: HMI input commands, → PLC analysis and execution, → feedback of the operating status to the HMI display.

2. How to simplify operations? 6 core scenarios
1. Parameter preset and one-click call
• Traditional pain points: Different materials (such as PET film vs copper foil) need to manually adjust dozens of parameters such as tension, speed, tool pressure, etc.
• Smart Solution:
◦ PLC stores multiple sets of recipes (such as "lithium battery separator -12μm"), and the HMI interface can be called with one click.
◦ Support parameter grouping display (basic/advanced) to avoid misoperation by non-technical personnel.
• Efficiency improvement: Changeover time reduced from 30 minutes to 2 minutes.
2. Automated process control
• Typical process:
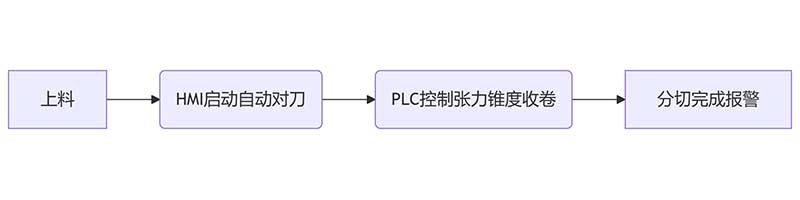
• PLC Logic:
◦ Automatically complete tool calibration, material correction, waste edge peeling and other actions to reduce manual intervention.
◦ Abnormal (such as material failure) triggers PLC shutdown and prompts the fault point (HMI pop-up window).
3. Real-time monitoring and adaptive adjustment
• HMI Dashboard:
◦ Dynamically display key data: current speed (m/min), tension (N), slitting width deviation (μm).
◦ Trend charts record historical data (e.g., tension fluctuations over an 8-hour period).
• PLC closed-loop control:
◦ The torque of the winding motor is adjusted in real time through encoder feedback to compensate for the elastic deformation of the material.
4. Fault diagnosis and predictive maintenance
• PLC Intelligent Diagnosis:
◦ Compare current/vibration sensor data with thresholds to predict tool wear (e.g., a 10% increase in spindle current triggers an early warning).
◦ The HMI displays a fault tree (e.g., "E07: Guiding Sensor Signal Loss").
• Reduced downtime: 50% faster maintenance response.
5. Authority management and standardization
• HMI Multi-Level Account:
◦ Operator: Only start/stop and basic parameter adjustments are allowed.
◦ Engineer: PLC logic and calibration parameters can be modified.
• Error-proofing design: PLC enforces the range of key parameters (e.g., tension should not exceed 80% of the tensile strength of the material).

6. Remote collaboration and data integration
• IoT Expansion:
◦ PLC data is uploaded to the MES system via OPC UA for production traceability.
◦ Mobile APP synchronizes HMI alarm information (VPN secure connection required).
3. Practical application cases
Case 1: Intelligent transformation of film slitting machine
• Before transformation: relying on the experience of the master to manually adjust the machine, the rejection rate is 5%.
• After:
◦ Siemens S7-1200 PLC + Velun HMI.
◦ HMI interface with integrated "Expert Mode" (hidden parameter password protection).
• Effect: The scrap rate is reduced to 0.3%, and novices can get up to work quickly.
Case 2: Metal foil slitting machine
• Challenge: The foil is prone to wrinkles and requires dynamic adjustment of the lateral pressure.
•Solution:
◦ PLC calculates the ductility of the material in real time, and links the pneumatic pressure roller.
◦ HMI displays a pressure heat map to assist in process optimization.

Fourth, the direction of future upgrades
1. AI support: The PLC integrates a lightweight AI module to automatically learn the optimal slitting parameters (such as the adaptive tension curve for new materials).
2. AR assistance: The HMI is superimposed with AR guidance, and the camera can identify the deviation of the tool installation angle.
3. Voice interaction: HMI supports voice commands (e.g. "speed up to 200m/min").
Summary: The operation of smart slitting simplifies the logic
| Traditional operations | PLC+HMI solution | User Benefits |
| Empirical trial adjustments | One-click call to the recipe library | Reduce technology dependency |
| Dashboard + button operation | Graphical touch controls | 70% reduction in mishandling |
| Disassemble the machine after the fault and troubleshoot | The HMI directly locates the faulty module | 60% reduction in repair time |
| Paper-based documentation of production data | Automatically generate electronic reports | Traceability efficiency increased by 90% |
Through the in-depth collaboration between PLC and HMI, the operation of the slitting machine has shifted from "craftsman dependence" to "standardized intelligent control", which has become a typical scenario for the implementation of Industry 4.0.
 Small slitting, big profits: explore the technical moat of ribbon slitting machines
Small slitting, big profits: explore the technical moat of ribbon slitting machines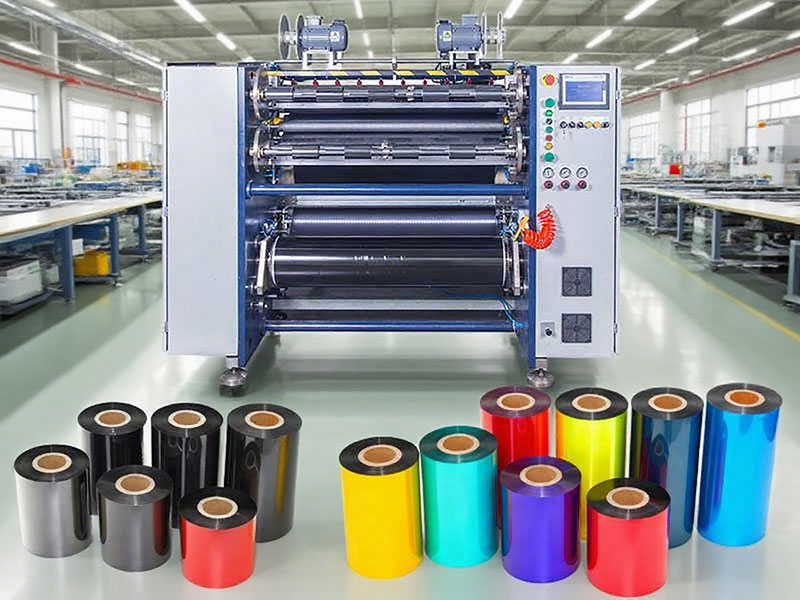 Precise slitting, efficiency doubled - a complete guide to ribbon slitting machine purchase
Precise slitting, efficiency doubled - a complete guide to ribbon slitting machine purchase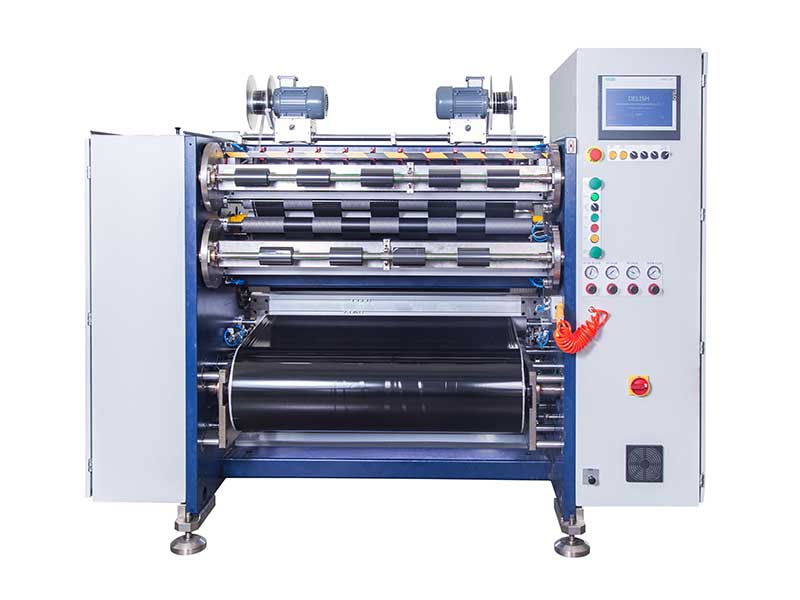 Stability overrides everything: Practical analysis of automatic ribbon slitting machine
Stability overrides everything: Practical analysis of automatic ribbon slitting machine Protecting the "seven layers of skin": How does the solar film slitting machine avoid precision coating damage?
Protecting the "seven layers of skin": How does the solar film slitting machine avoid precision coating damage? PET Film Slitting Machine Selection Guide: Key Features Determine Production Efficiency
PET Film Slitting Machine Selection Guide: Key Features Determine Production Efficiency